Learn how to diagnose type 2 diabetes with key tests like A1C, glucose tolerance, and fasting blood sugar. Early detection helps manage your health with tools like CGM and HealD X.
Heald Membership: Your Path to Diabetes Reversal
Table of content
Did you know? Type 2 diabetes is one of the most common chronic conditions worldwide, affecting 95% of the 830 million people (as per WHO, 2022). It changes how your body processes blood sugar (glucose), which is the primary energy source for your cells. But don’t worry—early diagnosis can help you take control and prevent complications down the road.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the simple steps to diagnose type 2 diabetes, explore the most common tests, and explain how medical professionals classify it using ICD-10 codes. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors is also essential in identifying type 2 diabetes early, so you can take proactive steps toward better health. Let’s dive in!
Diagnosis Criteria for Type 2 Diabetes
Doctors use specific diagnostic criteria to determine whether you have type 2 diabetes, are at risk (prediabetes), or have normal blood sugar levels. These criteria ensure a consistent and accurate approach to identifying the condition.
Think of it like a checklist! Your healthcare provider uses these tests to uncover what's happening in your body:
A1C Test
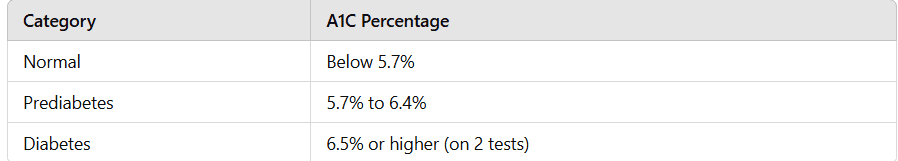
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1c test, measures the average blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months. It is a standard and non-invasive method for diagnosing diabetes.
How it works: The test measures the percentage of hemoglobin coated with sugar (glycated hemoglobin).
Diagnostic thresholds:
Normal: Below 5.7%
Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
Diabetes: 6.5% or higher on two separate tests
Why A1C is a reliable indicator:
Provides a long-term view of blood sugar levels
No need for fasting
Convenient for screening and monitoring diabetes progression
Glucose Tolerance Test
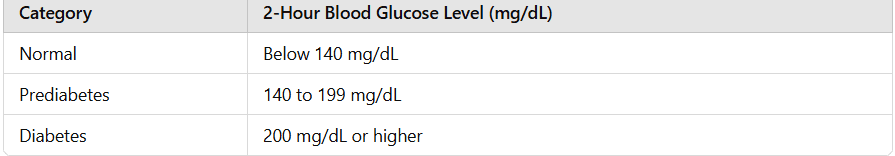
The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) is another tool to diagnose type 2 diabetes, especially when results from other tests are inconclusive.
How it works: After fasting for at least 8 hours, the patient drinks a glucose-rich beverage. Blood sugar levels are measured at fasting, 1 hour, and 2 hours post-consumption.
Diagnostic thresholds:
Normal: Below 140 mg/dL after 2 hours
Prediabetes: 140 to 199 mg/dL
Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher
When is OGTT recommended?
When other test results are borderline
During pregnancy to screen for gestational diabetes
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
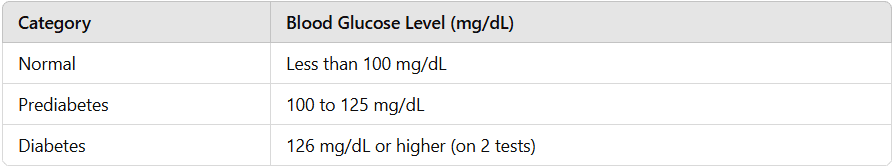
This simple test measures blood sugar levels after fasting overnight (8–12 hours). It is often used as an initial screening tool.
Diagnostic thresholds:
Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
Prediabetes: 100 to 125 mg/dL
Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests
Limitations:
Only captures a snapshot of blood sugar at a specific time
May miss fluctuations that other tests like A1C can detect
Random Blood Sugar Test
This test measures blood sugar levels at any random time during the day. A reading of 200 mg/dL or higher, accompanied by symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, or unexplained weight loss, suggests diabetes.
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 Diabetes
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), is a standardized coding system used in healthcare to classify diagnoses and procedures. For type 2 diabetes, the ICD-10 code is E11. This category is further divided to include specific complications and manifestations:
E11.9: Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications
E11.21: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy
E11.22: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with chronic kidney disease
E11.65: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia
Why is ICD-10 important?
Facilitates accurate billing and insurance claims
Helps in monitoring public health trends
Supports research and resource allocation for diabetes care
Understanding the Role of Glucose Monitoring
Effectively managing type 2 diabetes involves understanding how your daily habits—like eating, exercising, and even sleeping—impact your blood sugar levels. Glucose monitoring tools play a pivotal role in this process by providing valuable, real-time insights.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): A Game Changer
One of the most effective tools for monitoring glucose levels is a Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) device, such as the Dexcom Stelo CGM (just at $89). Here’s how it works and why it’s essential:
Real-Time Monitoring: Tracks your glucose levels throughout the day and night, offering a comprehensive view of your glucose trends.
No Finger Pricks: Unlike traditional glucometers, CGM devices like Stelo eliminate the need for painful and inconvenient finger pricks.
Smartphone Integration: The Stelo CGM syncs with your smartphone, providing easy-to-read graphs and data insights.
Proactive Alerts: Get notified when your glucose levels are too high or too low, allowing for timely interventions.
Personalized Insights: Understand how your body responds to specific foods, activities, and sleep patterns.
Enhancing CGM Insights with Heald X
While CGM devices provide critical data, pairing them with programs like Heald X offers even greater benefits:
Integrated Data Tracking: Sync the Dexcom Stelo CGM with the Heald X platform for a comprehensive view of your health.
Lifestyle Recommendations: Receive personalized suggestions based on your glucose trends to improve diet, sleep activity, and overall health.
Progress Monitoring: Track goals and see measurable improvements in your glucose control over time.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters: Preventing Complications
Detecting type 2 diabetes early is crucial. It can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications, including:
Heart Disease: Diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and strokes.
Nerve Damage: High glucose levels over time can damage nerves, leading to pain or numbness, especially in the hands and feet.
Kidney Damage: Diabetes can harm the kidneys, potentially leading to chronic kidney disease.
By identifying diabetes early, individuals can adopt lifestyle changes, start appropriate treatment, and monitor their progress effectively.
The Heald Approach to Early Intervention
Heald’s personalized health program, HealdX focuses on early intervention by offering tools like CGM integration, nutrition coaching, and expert guidance. These features help users understand their risk factors and take action before complications arise.
When Should You Get Tested? A Simple Checklist
You might wonder, “Should I get tested for diabetes?” Here are common scenarios where testing is recommended:
Overweight or Obesity: Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor.
Family History of Diabetes: Genetics play a role, so it’s wise to get tested if a close relative has diabetes.
Age 45 or Older: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age.
Symptoms of Diabetes: Experiencing frequent urination, extreme hunger, fatigue, or blurry vision are red flags.
High Blood Pressure or Cholesterol Levels: These often go hand-in-hand with diabetes risk.
Pregnancy: Pregnant women should be screened for gestational diabetes to protect both mother and child.
If any of these factors apply to you, schedule a screening with your healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts: Empowering Your Diabetes Journey
Taking charge of type 2 diabetes starts with understanding your body—diagnostic tests like the A1C and glucose tolerance test give you clarity, but the real game-changer is how you manage it long-term. With tools like the Dexcom Stelo CGM and programs like Heald X, you get the best of both worlds: advanced glucose monitoring and tailored insights that simplify the journey. Start by evaluating your risk factors, consulting your doctor, and exploring smart tools that turn complex data into easy-to-follow action plans. Managing diabetes doesn’t have to be overwhelming—it’s about making smarter choices, one step at a time, for a healthier, brighter future.

Sandeep Misra is the Co-Founder and Chief Growth Officer at Heald, where he leads growth strategy and partnerships for data-driven programs focused on diabetes reversal and metabolic health. He brings over two decades of experience across healthcare technology, population health, and enterprise partnerships, having held senior leadership roles at AWS, Rackspace, and NTT Data.
Popular Blogs
Comments









