Prevent diabetes complications with regular monitoring, blood sugar control, and healthy lifestyle choices. Heald offers personalized coaching, AI tools, and behavioral support to help you achieve your health goals.
Heald Membership: Your Path to Diabetes Reversal
Table of content
Diabetes is a complex and chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The complications that arise from poorly managed diabetes can significantly impact the quality of life. As an endocrinologist, I’ve witnessed the profound effects diabetes can have on eye, kidney, and nerve health. However, with proper management and a proactive approach, these complications can be prevented or delayed. In this blog, we will delve into practical strategies to prevent diabetes complications, focusing on lifestyle changes, weight loss, and the role of a coach, nutrition, AI, and behavioral psychologists in achieving diabetes reversal.
So, let’s get started!
Join our webinar to learn more about managing diabetes and protecting your heart health!
Understanding Diabetes Complications
Diabetes, particularly when not well-controlled, can lead to severe complications. These complications are often categorized into microvascular and macrovascular complications. Microvascular complications include retinopathy (eye damage), nephropathy (kidney damage), and neuropathy (nerve damage). Each of these complications can profoundly affect a person's health and well-being. In contrast, macrovascular complications involve larger blood vessels and can lead to cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. It is essential to understand the underlying mechanisms of these complications to effectively prevent and manage them.
Microvascular complications arise due to prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels, which leads to damage in the small blood vessels. The high glucose levels can cause these blood vessels to leak or become blocked, disrupting the normal supply of blood and nutrients to tissues. This results in tissue damage and the onset of various complications.
On the other hand, macrovascular complications are linked to the buildup of atherosclerotic plaques in the large arteries, driven by the combined effects of hyperglycemia, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. This buildup narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow, potentially causing life-threatening events like myocardial infarctions and strokes.
Eye Health: Preventing Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness among adults. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the inner eye. The retina is crucial for vision as it converts light into neural signals that are sent to the brain. When the retinal blood vessels are damaged due to prolonged high blood sugar, it can lead to swelling, leakage, and, in severe cases, new blood vessel formation, known as proliferative retinopathy. Over time, this can lead to vision loss if not properly managed.
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy:
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR): This early stage is characterized by microaneurysms (small bulges in the blood vessels of the retina that often leak fluid), dot hemorrhages, and retinal swelling. Patients may not experience symptoms during this stage, making regular eye exams critical for early detection.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR): This more advanced stage involves the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels on the retina and the vitreous (the clear gel that fills the inside of the eye). These new vessels can bleed, causing vitreous hemorrhage, and may also lead to scar tissue formation, which can cause retinal detachment. PDR significantly increases the risk of severe vision loss.
Prevention Strategies:
Regular Eye Exams: Annual comprehensive eye exams are crucial. Early detection of retinopathy can prevent severe vision loss. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes have an eye exam at least once a year.
Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining blood glucose levels within the target range is essential. Studies have shown that good blood sugar control can delay the onset and progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Blood Pressure Management: High blood pressure can exacerbate retinopathy. Keeping blood pressure under control can reduce the risk of eye complications.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: A balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, combined with regular physical activity, can improve overall eye health.
Kidney Health: Preventing Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication that can lead to kidney failure. High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys' filtering system, causing protein leakage into the urine, a condition known as albuminuria. If untreated, nephropathy can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
The kidneys filter waste products and excess substances from the blood, which are then excreted in urine. In diabetes, elevated blood glucose levels can damage the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys (glomeruli). This damage reduces the kidneys' ability to filter waste effectively, leading to a buildup of toxins in the blood and protein leakage into the urine. Over time, this can cause the kidneys to lose their filtering capacity entirely.
Risk Factors:
Duration of Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing nephropathy.
Blood Sugar Levels: Poor blood glucose control increases the risk of kidney damage.
Hypertension: High blood pressure is both a cause and a consequence of kidney disease.
Genetic Predisposition: Family history of kidney disease can increase risk.
Smoking: Smoking exacerbates kidney damage and accelerates the progression of nephropathy.
Prevention Strategies:
Regular Kidney Function Tests: Annual tests to monitor kidney function, including urine albumin and serum creatinine levels, can detect early signs of nephropathy. Microalbuminuria (small amounts of protein in urine) is often the first indicator of kidney damage. Early detection allows for timely intervention to slow disease progression.
Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure Control: Keeping blood sugar and blood pressure within target ranges is critical. The American Diabetes Association recommends maintaining an HbA1c level below 7%. The use of medications like ACE inhibitors or ARBs can help protect the kidneys by reducing blood pressure and preventing further kidney damage.
Diet and Nutrition: A diet low in sodium and rich in vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins supports kidney health. Reducing sodium intake helps manage blood pressure, and adequate protein intake supports kidney function without overloading it. Consulting with a nutritionist can provide personalized dietary recommendations to meet individual health needs.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking can worsen kidney damage. Quitting smoking is one of the best steps toward preventing diabetic nephropathy. Smoking cessation reduces the progression of kidney disease and improves overall health outcomes.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of hypertension and improves overall kidney health. Weight loss, even a modest amount, can have significant benefits for kidney function.
Medications and Regular Monitoring: Use prescribed medications as directed and monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels regularly. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help manage risk factors and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Curious about your food portions? Use our Nutrition Analyzer to compare portions and understand calorie impacts!
Research-Based Insights on Diabetic Complications
A pivotal study known as the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) has significantly advanced our understanding of the relationship between blood glucose control and the prevention of diabetic complications. Conducted over a decade, this landmark research demonstrated that intensive blood glucose control markedly reduces the risk of microvascular complications, including retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. The DCCT involved 1,441 participants with type 1 diabetes who were randomly assigned to either intensive therapy (aiming for near-normal blood glucose levels) or conventional therapy (standard diabetes care).
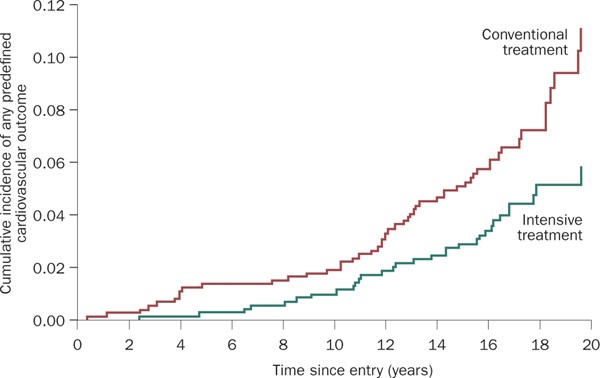
The results were compelling: those in the intensive therapy group experienced a 76% reduction in the risk of retinopathy, a 50% reduction in the risk of nephropathy, and a 60% reduction in the risk of neuropathy compared to those in the conventional therapy group. These findings underscore the critical importance of maintaining tight blood glucose control in preventing the severe complications associated with diabetes. The study’s implications have been further validated by the follow-up Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study, which confirmed long-term benefits of early intensive therapy in reducing the incidence of these complications over time.
Nerve Health: Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels. It often affects the legs and feet, leading to pain, numbness, and even serious infections. Neuropathy can severely impact mobility and quality of life, making prevention and management crucial.
Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy occurs when high blood sugar damages the nerves throughout the body. The condition can manifest in various forms, including peripheral neuropathy (affecting the extremities), autonomic neuropathy (affecting internal organs), and focal neuropathy (affecting specific nerves).
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy:
Peripheral Neuropathy: The most common type, affecting the feet and legs first, then possibly the hands and arms. Symptoms include tingling, pain, numbness, or weakness.
Autonomic Neuropathy: Affects the nerves controlling internal organs, leading to issues such as digestive problems, bladder and sexual dysfunction, and heart rate abnormalities.
Proximal Neuropathy: Affects the thighs, hips, or buttocks, causing pain and muscle weakness.
Focal Neuropathy: Affects specific nerves, leading to sudden weakness or pain in any part of the body.
Prevention Strategies:
Regular Foot Exams: People with diabetes should check their feet daily for cuts, blisters, and sores, which can lead to infections if not treated promptly. Regular visits to a podiatrist for comprehensive foot exams can help prevent complications. Wearing properly fitting shoes and maintaining good foot hygiene are also essential.
Blood Sugar Control: Consistent blood sugar management is the most effective way to prevent nerve damage. Studies have shown that tight glucose control can reduce the risk of neuropathy by up to 60%. Aim for an HbA1c level below 7%, or as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce the risk of neuropathy. Weight loss, even a modest amount, can significantly improve nerve function and overall health. Regular physical activity improves circulation, which is crucial for nerve health.
Pain Management: For those already experiencing neuropathy, pain management strategies, including medications, physical therapy, and alternative therapies (such as acupuncture), can improve quality of life. Medications like pregabalin, duloxetine, and gabapentin can help manage neuropathic pain. Physical therapy can help maintain strength and mobility.
Healthy Diet and Nutrition: A diet rich in vitamins and nutrients that support nerve health, such as vitamin B12, can help manage and prevent neuropathy. Avoiding alcohol and smoking can also reduce the risk of nerve damage.
Regular Monitoring and Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor blood sugar levels, foot health, and overall nerve function can help detect early signs of neuropathy and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
The Role of Lifestyle, Weight Loss, and a Diabetes Coach
Lifestyle and Weight Loss
A healthy lifestyle is the cornerstone of diabetes management. Weight loss, in particular, can have a profound impact on blood sugar control and overall health.
Strategies for a Healthy Lifestyle:
Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole foods, including vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Stress Management: Stress can affect blood sugar levels. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
The Role of a Diabetes Coach
A diabetes coach can provide personalized support and guidance, helping individuals stay on track with their health goals. Coaches offer accountability, motivation, and practical advice on managing diabetes through lifestyle changes.
Utilizing AI and Behavioral Psychologists
AI in Diabetes Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) can play a significant role in diabetes management. AI tools can analyze vast amounts of data to provide personalized recommendations, predict blood sugar trends, and remind patients to take their medications. These tools can enhance the effectiveness of diabetes management plans.
Behavioral Psychologists
Behavioral psychologists help individuals change unhealthy behaviors and adopt healthier habits. They use techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address emotional and psychological barriers to effective diabetes management. Working with a behavioral psychologist can help individuals develop sustainable habits that support long-term health.
Heald: Your Partner in Diabetes Management
At Heald, we understand the challenges of managing diabetes and the importance of preventing complications. Our comprehensive services include personalized coaching, advanced AI tools, and access to behavioral psychologists. We offer a holistic approach to diabetes management, focusing on lifestyle changes, weight loss, and nutrition.
Services Offered by Heald:
Personalized Diabetes Coaching: Our experienced coaches provide one-on-one support, helping you set and achieve your health goals.
AI-Powered Tools: Our AI tools offer personalized recommendations, medication reminders, and blood sugar trend analysis.
Behavioral Psychology Support: Work with our behavioral psychologists to develop healthy habits and overcome barriers to effective diabetes management.
Nutrition Counseling: Our nutritionists provide customized dietary plans to support your health and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Preventing diabetes complications is achievable with the right strategies and support. Regular monitoring, blood sugar control, healthy lifestyle choices, and the guidance of healthcare professionals are key to maintaining eye, kidney, and nerve health. At Heald, we are committed to helping you manage your diabetes effectively and prevent complications. Take control of your health today by booking an appointment with one of our experts.
Take control of your diabetes today. Book an appointment with one of our experts at Heald and start your journey towards better health and diabetes management.

Popular Blogs
Comments